Production methods in agriculture have always been strongly influenced by technical progres. Today, digitization and automation are advancing rapidly in many sectors of the economy and will change production processes and thus the world of work in the future. The question arises to what extent agriculture and horticulture can benefit from these developments in order to use new technologies to solve challenges of today's production systems. For example, resistance issues in plant protection are increasing while less and less effective plant protection products are available. In addition, the current agricultural and horticultural production systems are subject to public criticism due to concern on environmental impacts and animal welfare.
Therefore, we analyse and evaluate to what extent new technologies in agriculture and horticulture help to overcome these challenges. For this purpose, we investigate the following questions:
How do new technologies affect production systems, farm management and the competitiveness of agricultural and horticultural enterprises?
What can policy-makers do to ensure that new technologies lead to positive environmental impacts and avoid negative consequences?
How can new technologies be used to monitor the environmental impacts of agriculture?
Our research currently focusses on the benefits of precision farming in arable and horticulture, e.g. to reduce the use of pesticides and fertilisers. In addition, we integrate satellite data into our nationwide analyses of land use and land use changes in the agricultural landscape. For this purpose, we use data from the EU's Copernicus program as well as commercial high-resolution satellite images. The satellite data provide an important data basis for our monitoring activities, reporting obligations, policy evaluation and impact assessments (for more information, see Thünen Remote Sensing).
For our analyses we cooperate with many different universities, colleges and other research institutions, e.g. with the TU Braunschweig, the ATB, the DLRRheinpfalz or the Julius Kühn-Institut.









![[Translate to English:] HotSpots Erosion](/media/_processed_/d/3/csm_2510_20190524_Lamspringe_Erosion_Trompeterbusch_low_res_w_68439fae45.jpg)

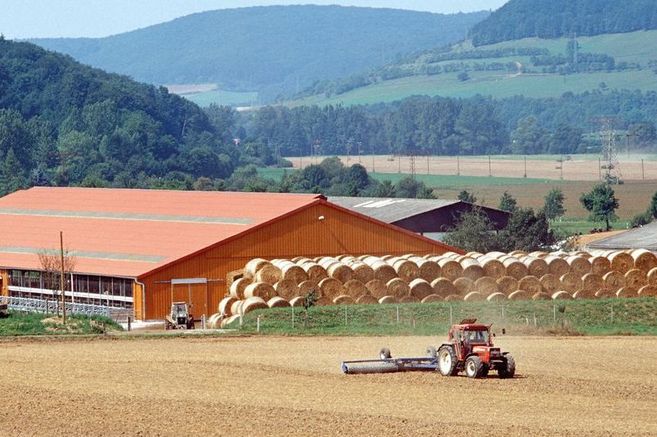
![[Translate to English:] International competitiveness and further development of production systems in arable farming](/media/_processed_/2/5/csm_2460_ipl-272__Fotolia_167128134_L_large_3f2a202092.jpg)


![[Translate to English:] Satellite-based Indicators for Monitoring Fen Re-wetting](/media/_processed_/1/5/csm_2724_Satellitenbasierte-Indikatoren_C-Hellmann_DJI_0076_ba59ce9f94.jpg)


![[Translate to English:] Autonomous agricultural machinery](/media/_processed_/a/f/csm_1467_Organigramm_b71261dda5.png)

![[Translate to English:] HortiCo 4.0](/media/_processed_/7/4/csm_HortiCo40_Logo_MitClaim_RGB_9f895ba1a5.png)