Conventional wood adhesives are still usually based entirely on petrochemicals and, in the vast majority of cases, contain harmful formaldehyde as a cross-linking agent. Against this background, bio-based and formaldehyde-free lignin-carbonate prepolymers were developed at the Thünen Institute of Wood Research and tested as wood adhesives.
Lignin, a by-product of pulp production, is produced in large quantities every year and is usually incinerated. The material use of lignin, e.g., as a bio-based adhesive, is particularly challenging due to its complex chemical structure, poor solubility, lack of reactivity, and inconsistent molecular weight distribution.
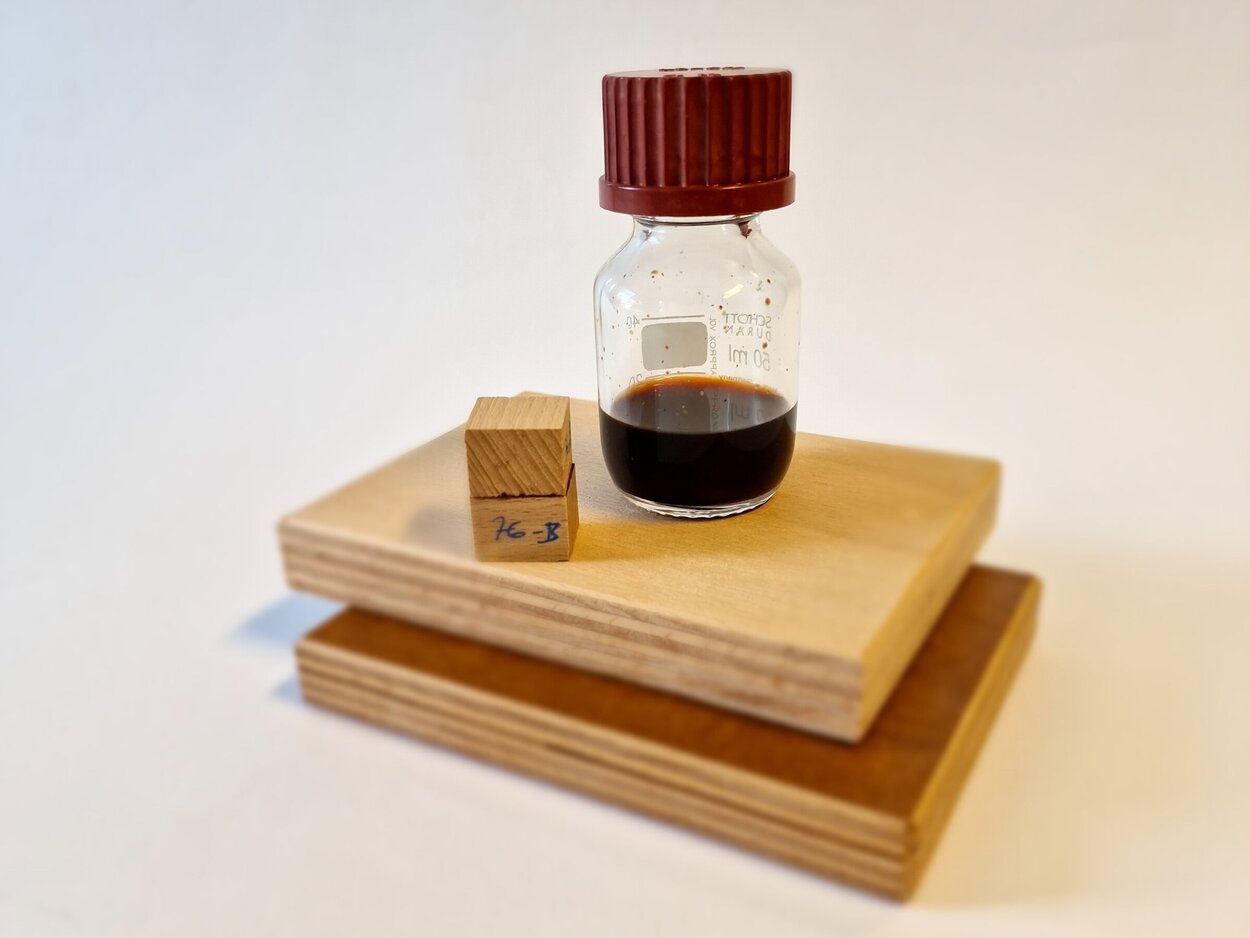
During the project, the powdered lignin was first pre-crosslinked with toxicologically safe multifunctional cyclic carbonates to form viscous prepolymers. Infrared- and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analyses and the determination of the molecular weight distribution of the prepolymers show that the cyclic carbonates were successfully attached to the lignin. This strategy makes the lignin soluble and facilitates application. At the same time, the lignin is activated by free carbonate groups.
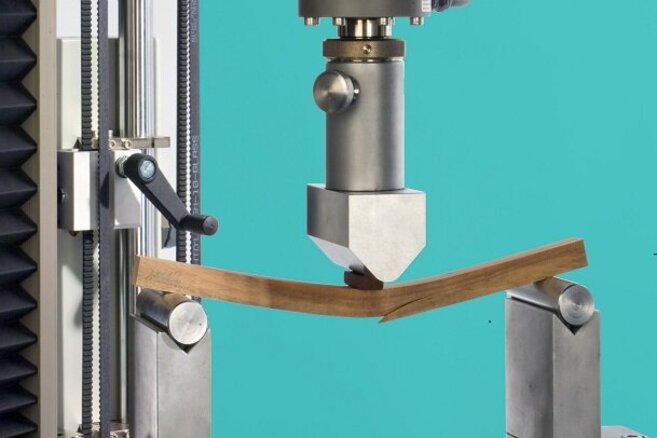
Bonding tests using the Automated Bonding Evaluation System (ABES) show that beech wood veneers can be successfully bonded with the prepolymers. At higher temperatures and longer pressing times, strengths in the range of phenolic resin references are achieved (5.8 - 6.2 N/mm²). The success of the bonding process depends less on the molecular weight of the prepolymer and more on the pressing time.
Further information:
Contact:
Dr. Nils Ortner