Project
Gillnet modifications to reduce bycatch (PEARLNET_OP)
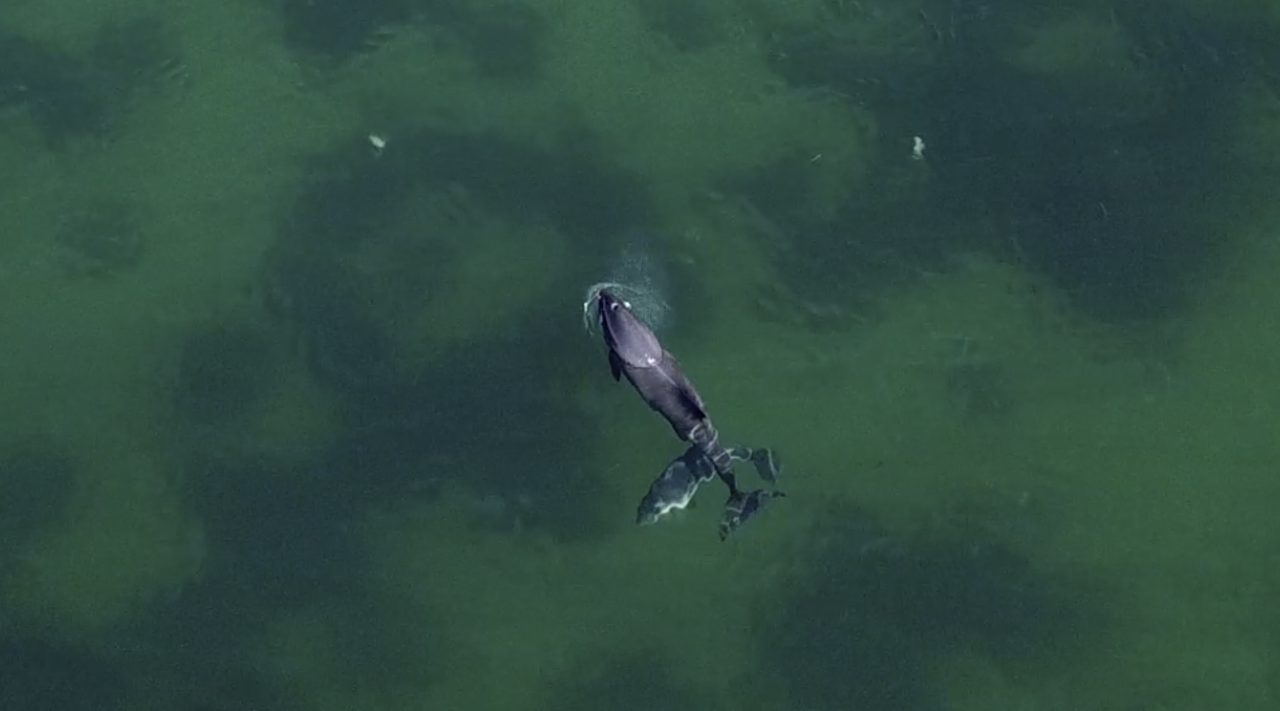

Using acoustically visible gillnets to reduce bycatch of harbor porpoises PEARLNET_OP (PEarls made from Acrylic glass could Reduce bycatch in gilLNETs – Observation of Porpoises)
To reduce bycatch of harbor porpoises in gillnets, an „acoustically visible“ gillnet (“PearlNet”) was developed. Within this projects, the behavioral reactions of harbor porpoises to the modified gillnet will be evaluated.
Background and Objective
Gillnets are one of most commonly used passive fishing gears worldwide. They have little to no sea bottom impact, are very size selective and are fuel-efficient due to their passive operating principle. Gillnets are made of a sheet of thin nylon netting with a light line on top (floatline) and a heavy line on the bottom (leadline). The nets stand like walls in the water column and fish should entangle in the netting.
Gillnets have been heavily criticized due to bycatch of marine mammals and other flagship species like diving seabirds, sharks and turtles. Globally, thousands of small cetaceans die annually in gillnets. In the Baltic Sea, the harbor porpoise is also affected by bycatch in gillnet fisheries.
Harbor porpoises echolocate to orientate themselves under water. This means, they emit acoustic signals (“clicks”) and perceive their surroundings via the echoes of these signals. Harbor porpoises are able to “see” the easily detectable floatline of gillnets, but do not appear to classify the netting as an impenetrable object. As a consequence they sometimes entangle and drown.
One way to reduce harbor porpoise bycatch could be to increase the acoustic detectability of the netting. This way, harbor porpoises could perceive the netting as a barrier and swim over or along the netting. Within the project STELLA, such a method to modify gillnets and make them acoustically visible was developed (Kratzer et al, 2020). Gillnets equipped with small (8 mm diameter) acrylic glass spheres (“PearlNet”) are highly acoustically visible. The spheres resonate at the echolocation frequency of the harbor porpoise and have thus a strong echo for their size.
Within the project PEARLNET_OP, we will carry out an experiment with the aim to understand the reactions of harbor porpoises to acoustically visible nets. Following the quantification of the behavioral reactions, a trial in the commercial fishery could be carried out.
Target Group
nature conservation, fisheries
Approach
In this experiment, the reaction of harbor porpoises to different types of gillnets will be investigated. To this end, the gillnet are set close to the coast and the reactions and swimming tracks of the porpoises are observed. The observation is carried out visually as well as with the aid of underwater acoustics (hydroacoustics).
To carry out such a behavior experiment and observe the porpoises successfully, the field site must meet the following requirements:
- Frequent, if not daily, occurrence of harbor porpoises
- High point of view from which the porpoises can be observed (e.g. a cliff near shore)
- Area is protected from wind and waves so that a prolonged observation time can be achieved
These criteria are met in Fyns Hoved located on the Danish island Fyn. Within PEARLNET_OP, the field trials will be carried out there in summer 2021.
The trials will comprise the following treatments:
- No net (control)
- Standard gillnet
- PearlNet
Data and Methods
Monitoring surfacing behavior of harbor porpoises using a theodolite is a wide spread method in marine mammal research. Theodolite are devices used in surveying technology. When a porpoise is surfacing to breathe, the position of the surfacing point is registered with the theodolite. As porpoise surface frequently within close distances, it is possible to track the swimming path of the porpoise.
A lot information can be gathered under water. For instances, changes in echolocation behavior and the position of the porpoise relative to the gillnet during diving can only be grasped if observation takes place in the water.
In PEARLNET_OP, two observation methods will be used. Firstly, the presence/absence of porpoises will be monitored using CPODs („Cetacean POrpoise Detectors“). CPODs are hydrophones that register the clicks of porpoises. From the registered signals it is possible to derive information regarding presence/absence as well as changes in click behavior, e.g. when they encounter the gillnet..
In addition to the CPODs there will be several hydrophone arrays installed close the the gillnets. Each array consist of four hydrophones that arranged in a certain way. When a porpoise echoloates towards the hydrophone arrays it is possible to derive the direction from which the animal is approaching (“triangulation”). This way, the underwater swimming path can be evaluated. Furthermore, the acoustic data will show whether porpoises echolocate more or less frequently when encountering acoustically visible nets.
Our Research Questions
- How does the behavior of harbor porpoises change when encountering an acoustically visible gillnet?
- Can these differences be documented visually as well as acoustically?
Results
During the field campaign that took place from June to August 2021, with nearly 200 hours of observation time, the three planned scenarios (No Net, Standard Gillnet, Pearl Net) were tested in roughly equal proportions. The number of observed animals ranged from 0 to 79 animals per day. Both visual (theodolite, drone) and acoustic data from the C-Pods suggest that harbor porpoises exhibited an earlier avoidance behavior in response to the Pearl Net compared to the Standard Net. There was no observed change in the typical behavior of the animals in the control scenario (No Net), where they freely moved through the experimental area during the test period.
The acoustic data recorded with Soundtraps promise a more detailed description of the animals' behavior but could not be conclusively completed within the project. Due to the ongoing high relevance of these data, further use and analysis may be possible within the currently running projects STELLA2 or PAL-CE.
Thünen-Contact

Involved Thünen-Partners
Involved external Thünen-Partners
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
(Seattle, WA, Vereinigte Staaten von Amerika) -
University of Massachusetts Dartmouth
(New Bedford, MA, Vereinigte Staaten von Amerika)
Funding Body
-
NOAA Fisheries: Bycatch Reduction Engineering Program (BREP)
(international, öffentlich)
Duration
7.2020 - 12.2022
More Information
Project funding number: NA20NMF4720276
Project status:
finished
Publications
- 0
Kratzer I, Stepputtis D, Santos J, Lütkefedder F, Stoltenberg A, Hartkens L, Schaber M, Kindt-Larsen L, Larsen F (2022) Angle-dependent acoustic reflectivity of gillnets and their modifications to reduce bycatch of odontocetes using sonar imaging. Fish Res 250:106278, DOI:10.1016/j.fishres.2022.106278
- 1
Kratzer I (2021) Gillnet modifications to reduce bycatch of harbor porpoises. DTU Aqua National Institute of Aquatic Resources, 172 p, Lyngby, Techn Univ of Denmark, Section for Ecosystem Based Marine Management, PhD Thesis
- 2
Kratzer I, Brooks ME, Bilgin S, Ozdemir S, Kindt-Larsen L, Larsen F, Stepputtis D (2021) Using acoustically visible gillnets to reduce bycatch of a small cetacean: first pilot trials in a commercial fishery. Fish Res 243:106088, DOI:10.1016/j.fishres.2021.106088

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/d/7/csm_Startseite-OF_03_c0dfd6e750.png)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/a/3/csm_20181116-151457-Stella-Jerome-Fischfalle-Warnem%C3%BCnde-Dorsche-im-Netzk%C3%A4fig-5691_heller_3050c72fa2.png)