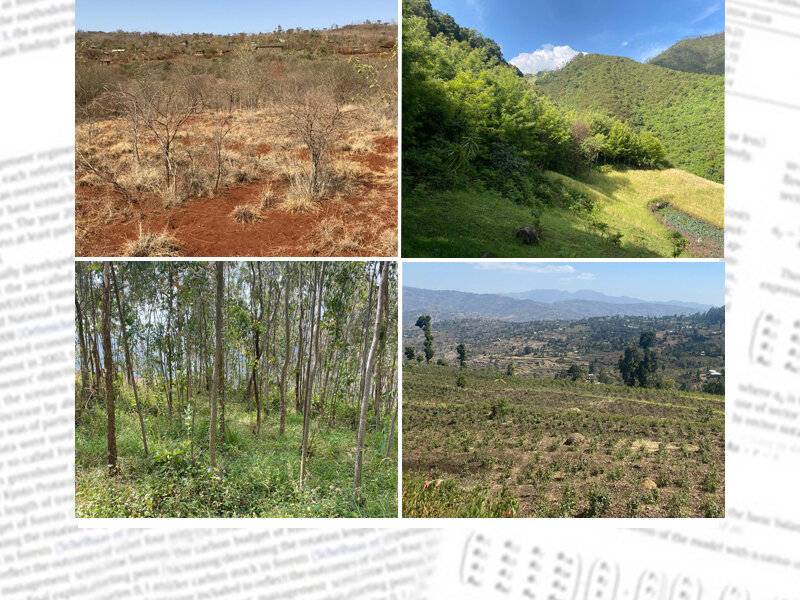
Passive restoration includes exclosures, either with or without management. Active restoration involves large- and smallholder tree plantations, as well as boundary planting. Performance is evaluated based on forest structure and biomass across different environmental clusters defined by soil, elevation, and climate.
The results reveal a strong influence of environmental clusters on the effectiveness of various restoration strategies.
The study, therefore, highlights where restoration success is more likely to be achieved based on environmental clusters and emphasizes the importance of appropriate management interventions in both passive restoration sites (Assisted Natural Regeneration) and active restoration strategies. It underscores the critical role of silvicultural management, selecting and aligning restoration strategies to specific site conditions, a concept that is vital to farmers, community members, government, non-government organizations, and other stakeholders engaged in restoration.
- Aleeje, A., Ahimbisibwe, V., Wellbrock, N., Ehbrecht, M., Günter, S., Schnell, S., Stanturf, J.A. and Bolte, A., (2025). Matching of forest restoration strategy to environmental conditions matters: evidence from south‐central Ethiopia. Restoration Ecology, p.e70144.
DOI: 10.1111/rec.70144. Aleeje A, Ahimbisibwe V, Wellbrock N, Ehbrecht M, Günter S, Bolte A (2025) Matching of restoration strategy to soil and other environmental conditions matters for forest landscape restoration: evidence from Ethiopia. Ecotropica 27:150, DOI:10.30427/ecotrop202501
https://literatur.thuenen.de/digbib_extern/dn069544.pdf- Projectsite
Forest Restoration